What is a Gas Leak Detector and How Does It Work

In industries where gas is essential for manufacturing, energy production, or heating, the risk of leakage poses a serious threat to property, personnel, and the environment. This is where a gas leak detector becomes a critical component in ensuring safety and regulatory compliance.
For industrial facility managers, engineers, and operations leaders, understanding how gas leak detectors function — and how to choose the right one — can make all the difference in operational security.
This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of gas leak detectors, how they work, types of detection technologies available, and key considerations for integrating them with systems like your gas meter.
What Is a Gas Leak Detector?
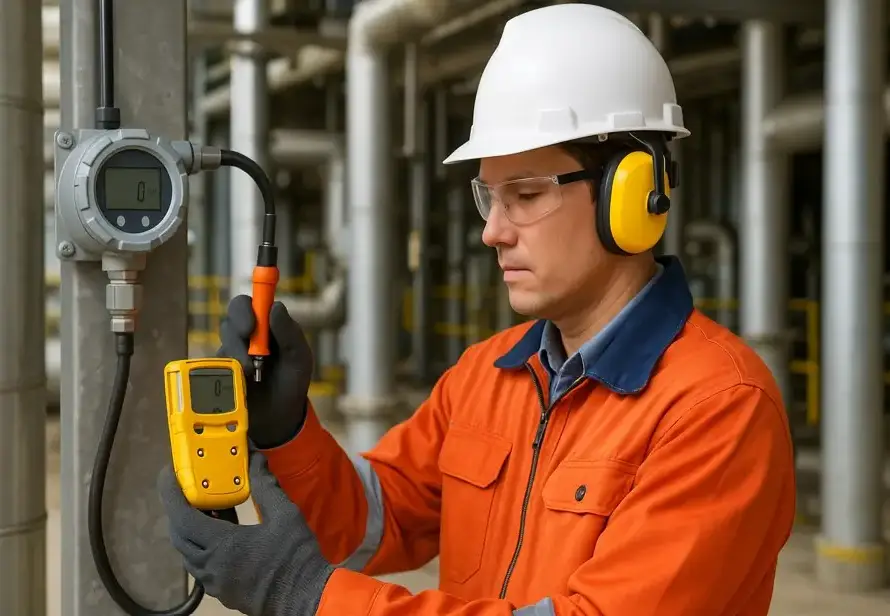
A gas leak detector is an electronic or mechanical device used to identify and alert users of the presence of hazardous gases in a specific area.
These detectors are designed to detect both combustible gases (such as methane, propane, and hydrogen) and toxic gases (like carbon monoxide or ammonia), depending on the application.
They are commonly installed in industrial environments, such as:
- Oil and gas processing facilities
- Chemical plants
- Manufacturing factories
- Laboratories
- Warehouses handling flammable substances
Why Are Gas Leak Detectors Important in B2B Settings?
For businesses in sectors like energy, petrochemical, and utilities, the presence of undetected gas leaks can result in:
- Explosions or fires
- Workplace injuries
- Environmental damage
- Production downtime
- Costly regulatory fines
These risks can be mitigated through the proper installation of reliable gas leak detection systems. When integrated with systems such as a gas meter, they provide a full picture of gas usage, anomalies, and possible points of failure in real time.
How Do Gas Leak Detectors Work?
Gas leak detectors operate by identifying specific gases present in the environment and triggering alerts when the concentration exceeds safe thresholds. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Detection
Each detector contains sensors specifically calibrated to detect one or more gases. When a target gas comes into contact with the sensor, it reacts and generates an electrical signal or resistance change proportional to the gas concentration.
2. Signal Processing
The signal is sent to a control unit or microcontroller. This component interprets the signal, converts it to a readable value, and compares it against preset alarm thresholds.
3. Alarm Activation
If the gas concentration exceeds safe levels, the detector activates an alert. This may include:
- Audible alarms (buzzers, sirens)
- Visual alerts (LED lights, display screens)
- Remote notifications (SCADA systems, SMS/email alerts)
4. System Integration
Advanced detectors are often linked with automation systems, fire suppression equipment, or gas meters to automatically shut off supply valves, log incidents, or initiate emergency procedures.
Types of Gas Leak Detection Technologies
There are various sensor technologies used in gas leak detectors, each suited for different gases and environments.
1. Catalytic Bead Sensors
- Detects combustible gases
- Works by oxidizing gases on a heated sensor
- Common in oil & gas and industrial plants
2. Infrared (IR) Sensors
- Detects hydrocarbon gases
- Measures absorption of infrared light
- Ideal for harsh or low-oxygen environments
3. Electrochemical Sensors
- Detects toxic gases (e.g., CO, NO₂, H₂S)
- Gases react with an electrode to produce a current
- Highly sensitive and precise
4. Photoionization Detectors (PID)
- Detects volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- Used in hazardous waste management and labs
5. Ultrasonic Detectors
- Detects high-frequency sound waves produced by pressurized gas escaping
- Doesn’t require direct gas-to-sensor contact
- Useful for open-air or high-pressure environments
Each type has its strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right detector often depends on the type of gas used, operating conditions, and the sensitivity required.
Key Features to Look For in a Gas Leak Detector
When sourcing a gas leak detector for industrial use, consider the following features:
Gas specificity
Ensure the detector is compatible with the types of gases present in your facility.
Detection range
Choose detectors that align with occupational exposure limits and safety guidelines.
Sensor lifespan
Look for long-life sensors with built-in calibration alerts.
Integration compatibility
Ensure the unit can integrate with your existing gas meter systems or building management software.
Certifications
Select detectors that meet local and international standards (e.g., ATEX, IECEx, UL).
Maintenance and calibration
Opt for models with easy access for sensor replacement and recalibration.
Common Applications Across Industries
Oil & Gas
Detect leaks in high-risk zones such as offshore platforms, refineries, and natural gas pipelines.
Manufacturing
Monitor chemical reactions, storage tanks, and high-pressure vessels.
Laboratories
Ensure proper air quality and safety during experiments involving volatile chemicals.
HVAC and Building Automation
In commercial buildings, gas detectors monitor leaks in heating systems or emergency generators.
Logistics and Warehousing
Detect flammable or pressurized gases stored in cylinders or transport units.
Integration with Gas Meter Systems
When paired with digital gas meters, gas leak detectors provide a powerful system for safety and operational control. Gas meters measure consumption, while detectors warn of unintended releases. Together, they:
- Reduce waste
- Prevent hazards
- Enable real-time diagnostics
- Help meet ESG and compliance targets
For example, an abnormal drop in gas meter readings combined with a leak alert could signal a rupture, enabling rapid shutdown and response.
Compliance and Safety Standards
In Malaysia and across Southeast Asia, regulatory bodies such as:
- Department of Occupational Safety and Health (DOSH)
- Suruhanjaya Tenaga (Energy Commission)
- International bodies like ISO, IEC, and OSHA
They have strict guidelines on gas leak detection systems, especially in commercial and industrial settings. It is essential to select products certified for explosion-proof and hazardous-area operation when required.
Maintenance and Calibration Best Practices
To ensure continued accuracy and compliance:
- Perform regular calibration checks (quarterly or per manufacturer guidelines)
- Replace sensors nearing end-of-life
- Keep maintenance logs for audits
- Train employees on alarm responses
Many advanced detectors include self-diagnosis features and connectivity to mobile apps or SCADA platforms to simplify maintenance.
Conclusion: Why Every Facility Needs a Gas Leak Detector
A gas leak detector isn’t just a safety device — it’s a critical part of any industrial risk management strategy. From protecting human lives and assets to ensuring regulatory compliance and operational continuity, these detectors deliver measurable ROI.
If your operations involve any form of combustible or toxic gas, investing in the right detection system — ideally integrated with your gas meter infrastructure — is no longer optional. It’s essential.