How Gas Pressure Regulators Work in Industrial Processes

Gas pressure regulators are a critical part of many industrial systems. Whether you’re running a chemical processing plant, manufacturing facility, or food production line, consistent and safe gas pressure is essential for both efficiency and safety.
In this guide, we’ll break down how gas pressure regulators work, the types used in industrial settings, how to select the right one, and maintenance best practices — so you can make informed decisions for your operations.
What is a Gas Pressure Regulator?
A gas pressure regulator is a mechanical device that reduces and controls the pressure of a gas from a high-pressure source to a lower, stable output suitable for downstream equipment.
Industrial processes require precise gas pressure control to:
- Prevent damage to machinery
- Maintain consistent product quality
- Ensure safety compliance
Unlike domestic regulators used for home appliances, industrial gas regulators must handle higher flow rates, wider pressure ranges, and tougher operating environments.
If you want to explore the full range of professional-grade regulators, check out our Gas Pressure Regulator product collection.
How Gas Pressure Regulators Work – Step-by-Step
Gas pressure regulators operate based on a simple principle: balancing inlet pressure with a control mechanism to maintain a stable outlet pressure. Here’s a step-by-step look:
1. Gas Enters the Regulator
High-pressure gas flows into the regulator through the inlet port.
2. Pressure Reduction via Valve Seat
Inside, a valve seat restricts gas flow based on the spring and diaphragm system’s position.
3. Spring and Diaphragm Control
- The spring pushes against the diaphragm to open the valve.
- As outlet pressure increases, it pushes back on the diaphragm, reducing valve opening.
4. Stable Output
This self-adjusting mechanism ensures the outlet pressure remains constant — even when inlet pressure fluctuates.
For a more detailed technical breakdown, visit our Gas Pressure Regulator page.
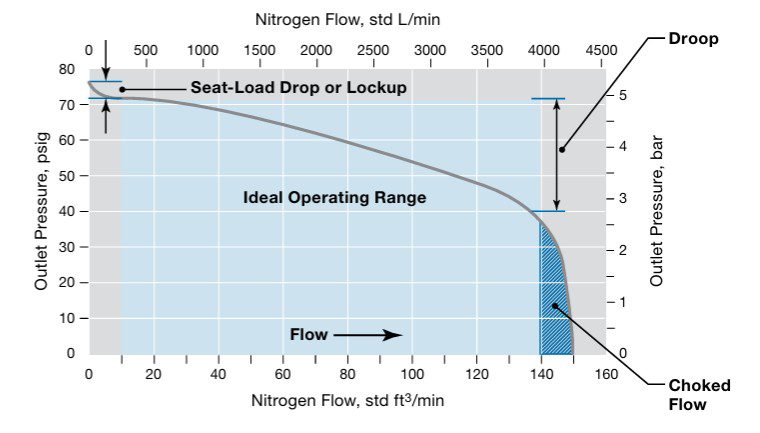
Understanding the Flow Curve of a Gas Pressure Regulator
Every gas pressure regulator has a flow curve that defines its operating range and regulating capacity. Understanding this curve is essential for selecting the right regulator for your application.
A typical flow curve is divided into three main sections:
1. Seat-Load Drop (Lockup)
This occurs when the outlet pressure rises slightly above the set point, causing the regulator valve (poppet) to close completely and stop gas flow. This protects downstream equipment from excess pressure.
2. Ideal Operating Range
The optimal section of the curve where the regulator provides the most stable control and maintains outlet pressure with minimal variation.
3. Choked Flow
A limiting condition where the regulator valve is fully open. In this state, further reductions in downstream pressure will not increase flow rate — meaning the regulator is no longer actively controlling pressure.
Regulator performance is often evaluated by plotting outlet pressure against flow rate. As flow rate increases, outlet pressure drops — a phenomenon called droop. The less droop a regulator has across its operating range, the more accurately it can maintain a set pressure.
Another key factor is the Supply Pressure Effect (SPE). As inlet pressure decreases — for example, when a gas cylinder nears empty — outlet pressure may rise slightly.
This can be managed by correctly sizing the regulator for the application and, in some cases, using two-stage regulation for greater stability.
For more information on sizing and selection, check out our Gas Pressure Regulator Selection Guide.
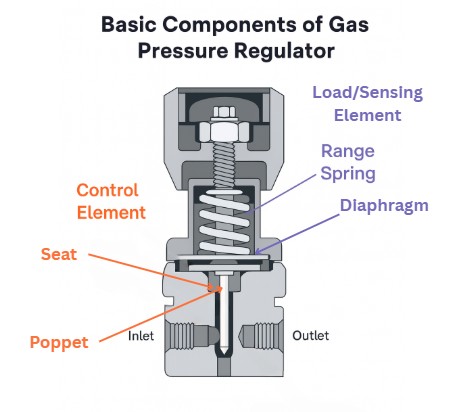
Main Components of a Gas Pressure Regulator
Component | Function |
Inlet Port | Entry point for high-pressure gas |
Valve Seat | Controls gas flow into the outlet |
Diaphragm | Senses outlet pressure changes |
Spring Mechanism | Applies force to adjust valve opening |
Outlet Port | Supplies reduced pressure gas to equipment |
Vent | Releases excess pressure for safety |
Tip: When choosing a regulator, always check if the materials are compatible with your gas type. For example, stainless steel for corrosive gases or brass for general industrial use.
Types of Gas Pressure Regulators for Industrial Use
Industrial gas regulators are designed to match specific process requirements. The main types include:
1. Single-Stage Regulators
- Reduce inlet pressure to desired outlet pressure in one step.
- Ideal for applications where inlet pressure doesn’t fluctuate significantly.
- Example: Supplying CO₂ to a packaging line.
2. Dual-Stage Regulators
- Reduce pressure in two steps for higher stability.
- Common in laboratory and precision manufacturing processes.
3. Dome-Loaded Regulators
- Use a controlled gas dome instead of a spring for extremely precise regulation.
- Suitable for high-flow or sensitive chemical processes.
4. Back Pressure Regulators
- Maintain a set upstream pressure by releasing excess gas when needed.
You can view our full Regulator product range to match your application.
Industrial Applications of Gas Pressure Regulators
Gas pressure regulators are used in almost every industry where gases play a role. Here are some real-world examples:
Industry | Example Application | Key Benefit |
Oil & Gas | Controlling natural gas flow to burners | Prevents surges and equipment damage |
Food & Beverage | CO₂ regulation in beverage carbonation | Ensures consistent taste and quality |
Chemical Processing | Precise delivery of reactive gases | Enhances safety and efficiency |
Pharmaceuticals | Inert gas blanketing for product storage | Prevents contamination |
Welding & Cutting | Controlling oxygen and acetylene supply | Improves weld quality and safety |
How to Choose the Right Gas Pressure Regulator
Choosing the correct regulator is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Here’s a checklist:
- Gas Type – Ensure compatibility with the regulator materials.
- Pressure Range – Match inlet and outlet pressure capabilities.
- Flow Requirements – Consider peak and continuous flow rates.
- Temperature Range – Check operating limits.
- Material Construction – Stainless steel, brass, or composite materials.
- Industry Standards – ISO, ASME, and relevant safety codes.
We’ve created a detailed Gas Pressure Regulator Selection Guide to help you choose the perfect unit for your needs.
Examples of High-Performance Gas Regulators
- 628H Comet High-Pressure Gas Regulator – Designed for demanding industrial use with exceptional stability.
- Coprim Regulator – Reliable performance for medium and low-pressure applications.
For additional performance benefits, read our article on High-Pressure Gas Regulator Benefits & Uses.
Common Gas Pressure Regulator Issues and Maintenance Tips
Like any mechanical component, regulators require maintenance to function optimally. Common issues include:
- Pressure Creep – A gradual increase in outlet pressure, often due to valve seat wear.
- Diaphragm Damage – Caused by contamination or material fatigue.
- Leakage – Usually from worn seals or incorrect installation.
- Contamination – Dirt or oil buildup can block passages.
Maintenance Tips:
- Install upstream filters for gas cleanliness.
- Schedule regular inspections.
- Replace diaphragms and seals periodically.
- Follow manufacturer service intervals.
Safety Guidelines for Industrial Gas Pressure Regulators
- Always use a pressure relief valve in high-pressure systems.
- Never exceed the manufacturer’s specified pressure limits.
- Ensure proper installation with correct torque settings.
- Store and handle regulators according to safety standards.
- Train operators in correct adjustment procedures.
For LPG-specific safety insights, read Are All LPG Gas Regulators the Same?.
Conclusion
Gas pressure regulators are the unsung heroes of industrial gas systems — providing consistent, safe, and precise control for a wide range of applications.
Choosing the right regulator and maintaining it properly can extend equipment life, improve safety, and boost process efficiency.
If you need expert help in selecting the best regulator for your industrial needs, contact us today at Comet Integrated for professional advice and a wide selection of high-quality regulators.



